There are many types of errors in Bethon. Regardless of where you are on the Bithon trip, you most likely faced one or more of these mistakes. For some, it may be easy to know the error in your code. For others? Not much. For this reason, explain what it means.
5
Horror
If you are an absolute beginner in Python or moved from a language like C/C ++ or Java, this will be the most common mistake you will face. In Python, we define the blocks using the hematic distance instead of brackets, as is common in many other languages. The “mass” indicates a portion of the code that is dealt with as one unit. Think about the conditional blocks, function or ring.
In Bethon, all phrases within the mass should have the same level of the hematic distance. When the level of the hematic distance (either increases or decreases) changes, it indicates the beginning or end of the mass. Bethon relies heavily on the consistent and consistent distance. The inconsistent, indulgent distance will lead to IndentationError.
A common scenario when you face this error is when you copy the icon of the young in your editor. Sometimes, due to the difference between how to coordinate the different editors, the indiscriminate distance may separate from one editor to another.
for i in range(5):
print(i)
While copying the above lines of the code, the bad distance erupted. Try to run this symbol will produce IndentationError. To fix this, you need to constantly distance the data under its collection.
for i in range(5):
print(i)
Another problem you may face regarding this error is to use tabs and distances. Some editors use signs of a tab, while others use four distances for the hemish. If you mix it in your software instructions, you will get an error. This one is more confused because it is difficult to see with the naked eye that contains signs of a tab and which contains spaces.
4
syntax
Each programming language has a sentence. In other words, a set of rules that you need to follow in order to write code in that language. So, if you cut any of these rules, the language does not know what you are trying to do and give you a mistake in building a sentence.
In Bethon, a SyntaxError It occurs when the translator finds a symbol that does not correspond to Python’s grammar. This means that the code is organized in a way that Beton cannot understand or implement. A SyntaxError It will prevent your program from starting. Some of the most common sentence construction errors that you will face in Bethon are:
-
Loss of punctuation (forgetfulness of the colon (:) When a symbol starts, such as conditional, rings or functions.)
-
Spelling or wrong errors for the main word Beton (writing
esleinstead ofelseUsingbreakA statement where it is not supposed to happen.) -
Using seized keywords as variable names.
-
Use of operators (using the duty operator (=) where the equal operator is supposed to be used (==) in a statement.)
-
Forget the end of the brackets or the end of a quote. This often happens when it works with multiple expressions and they are inside the interrelated brackets.
The good news is that the Python translator is completely intelligent enough to determine the type of sentence that it committed and indicates the line number, and even the approximate position of the error. Although the error message may sometimes be a little mysterious and does not reflect the exact cause. If you use a good icon editor or IDE, it can suggest the error and possible repairs.
3
Indexerror
Python offers many built -in data structures such as menus, tuples, and groups. We often need repetition through these data structures and access elements. Each data structure contains something called the index, which is the location of a specific element in this structure.
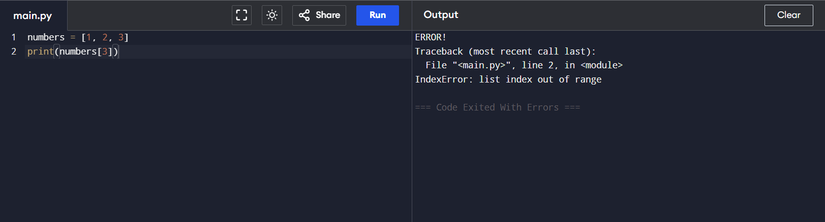
numbers = [1, 2, 3]
Here, we have a list called numbers. The way we can access the menu elements through its indicators, such as this:
print(numbers[1])
IndexError It usually occurs when trying to access an element in the data structure (also called a sequence) in an index outside the correct range of indicators of the data structure. In many programming languages, including Python, the index begins from scratch. Therefore, if the sequence contains N elements, the scope of indicators is from 0 to N-1.
Often, programmers forget to deal with a zero -based index and fall into a mistake from one, causing an index error. To avoid the index errors, always measure the length of your series.
if index < len(my_list):
Upon repetition through the sequence, the common Python error made by many programmers amends it as well. This also causes the index error. Therefore, avoid doing this.
2
Valuerror
Python offers many types of data. When working with different types of data, we need to deal with different literal values. Sometimes, we use it as functional media. What we need to know is that each function has a kind of expected data as a medium. When receiving this data, the function also realizes whether the value he received is valid.
This brings ValueError In Bethon. It is an integrated exception that is raised when you receive a function or intermediate operation that has the correct type of data but an inappropriate value. This means that the type of intermediate is acceptable, but its specific value is not valid for the operation that is carried out.
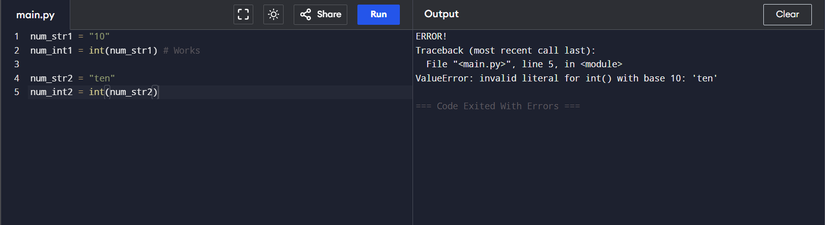
A very common condition so is when you want to convert the type of data to another.
int('10')
This transforms the series “10” into a correct number 10. However, if you do this:
int('ten')
You get a value error. This is because int() The function of the series is a chain data type. But the value of this chain must consist of numbers. That is why “ten” is an unacceptable value. Likewise, you may get this error when doing sports.
import math
math.sqrt(-5)
the sqrt() A job expects a positive number. Therefore, the negative number as a medium will raise the value of the value. Another common scenario for facing value errors is when you take the user’s entry. Since you do not have any control in what the user can enter, writing a wrong value will lead to a mistake.
The best way to deal with it ValueError Using attempt blocks.
try:
num = input("Enter a number: ")
num_int = int(num)
except ValueError as e:
print(f"Caught a ValueError: {e}")
In this way, you can prevent the program’s failure even if the user enters the wrong value.
1
Bacheloon
the AttributeError It is a common exception in Python when trying to reach a characteristic or method that is not present on a specific object. In simple phrases, this means that you are asking an object to do something that is not designed to do it.
Whether you work with strings, lists, or custom groups, it is easy to assume that an object has certain properties or capabilities, especially when switching between different types of data. However, Bethon will raise AttributeError The moment when you try to summon an unavailable feature.
text = "hello world"
print(text.push())
The strings do not have any push() road. Therefore, in the above example, you will get an error in the characteristic. Here is another example:
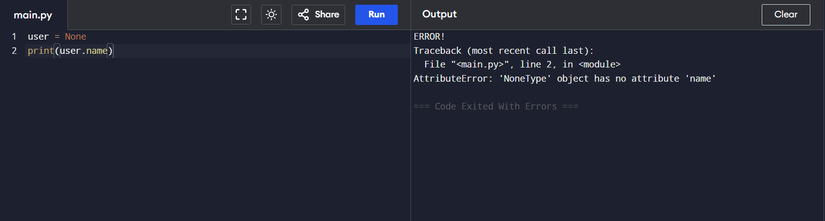
user = None
print(user.name)
Try to reach the “name” feature on a NoneType The object will also lead to this error. In all these cases, the object that works with it simply does not support the feature you are trying to reach. To prevent this error from boycotting your program, consider checking the types of objects.
type(obj)
isinstance()
Built -in dir() The job reveals all the correct features and methods available on an object. It will teach you to use it on your being, what are the features you can use.
Python being an easy language, very easy to learn the basics of language. Now that you have known some common mistakes, you will be able to correct them and write more code for the second without any concerns.