
Microorganisms have formed the ground for about four billion years. At least a trillion microbiology that maintains the biomas – for example, by producing oxygen or carbon insulation1. Microbes are thrived in harsh environments and used various energy sources, from methane to metals. They can stimulate complex reactions under the surrounding temperatures and pressure noticeably.
The possibility of exploiting these microbial capabilities to reduce the impact of human activities on this planet has been greatly recognized2. Bacteria or fungi are already used to produce materials and types of fuel and fertilizers in ways to reduce energy consumption and use fossil fuels, as well as to clean wastewater and pollutants3.
Despite its extensive capabilities, microbes -based techniques remain largely ignoring them in international climate change plans or reducing biological diversity loss.4. For example, discussions on the role of microbial technologies in achieving alternatives free of fossils for current products and operations were small or absent in United Nations Conferences of the Parties (COPS) in 2023 and 2024 on climate change, and on biological diversity in 2022 and 2024 (see nature 63617-18; 2024).
Is Cop29 Ceal Deal as a historical penetration or disappointment? Researchers interact
To improve the benefit of microbiology in the face of climate change and other challenges of sustainability, we gathered the International Federation of Microbiological Associations and the American Association of Microbiology (Authors) in December 2023-as a group of microbial biology specialists, public health and economic scientists who have experience in health, energy, greenhouse agriculture, soil, and soil. In a series of meetings, we evaluated whether some of the microbial technologies that are already in the market can contribute to sustainable, ethical, ethical and economic solutions economically. We have identified cases where the technical feasibility of the approach has already been clarified, which can become competitive solutions with the al-Hawour-based approach today in 5-15 years.
This work convinced us that microbial interventions provide a great promise as technological solutions to address climate change-by reducing pollution and the loss of global biological diversity. Here, we explain why it can be very important5 Highlighting some issues that we believe are microbiologists, climate scientists, environmental scientists and public health scientists, as well as companies, economists and politics, they will need to consider spreading such solutions on a large scale.6.
The possibilities of microbes
The use of genetic tools, vital engineering and progress in artificial intelligence greatly enhances Researchers’ capabilities to design proteinsAnd microbes or microbial societies. Using these and other methods, microbiologists can help treat three main problems.
First, many products manufactured from fossil fuel (energy, fuel and other chemicals) can be produced by “feeding” microbes with waste plastic, carbon dioxide, methane or organic materials such as sugar cane or wood chips.
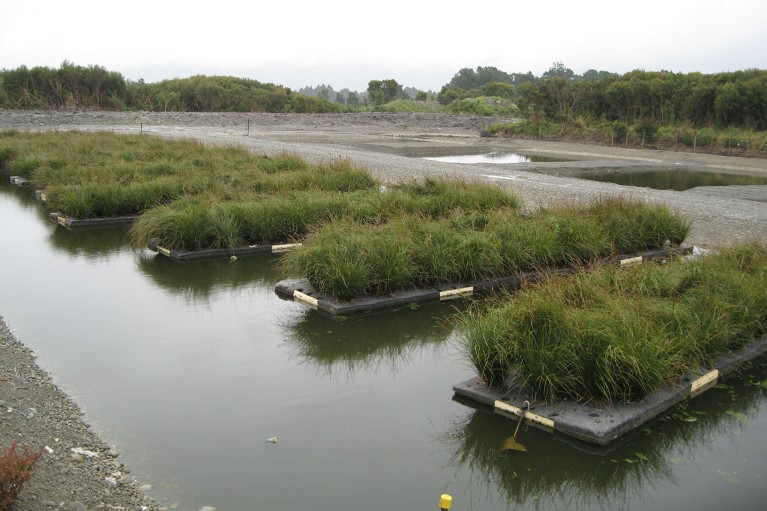

Microbes that grow under the synthetic islands can transform lakes from clear methane sources to carbon basins.Credit
Among the many companies that apply the microbial solutions to process climate change, Lanzatech, a carbon riding company in Skokie, Illinois, operates on a commercial flying fuel from ethanol produced when investigating microbes in industrial waste gases or sugar cane. At the same time, the company Natureworks In Pleimmouth, Minnesota, polymers, fiber and biological plastic are produced using microbial fermentation of primary diseases, such as kusava, sugar cane and beets.
Second, microbes can be used to clean pollution – from greenhouse gases, raw oil, plastic and pesticides to medications.
For example, a startup named Carbios, based in Cleremont Firand, France, developed a modified bacterial enzyme It collapses and recycles polyethylene terefaiti (PET), one of the most common plastic materials. Another company – International eating oil spills In Dallas, Texas-Microbial uses to clean oil spills, and large waste management companies in North America use bacteria called methanotrov to convert methane produced from the landfill (greenhouse gas is more powerful than CO2In ethanol, biofuels, polymers, decomposing plastic materials and industrial chemicals.

Children’s exercise? Trump’s climate policies will hurt – But the green transition is underway
Company Al Jazeera International Fall In Shepherd, Montana, even building artificial islands floating on lakes and cabinets that have been contaminated through excessive nutrient flow, so that microbes that consume methane (which colonizes the underside of the islands) can remove methane from the lake deposits. In this case, the goal is to convert the internal lakes and tanks from net sources of methane to carbon basins.
Finally, microbes can be used to make food production less dependent on chemical fertilizers and more sustainable.
The chemical process needed to produce ammonia for fertilizers include burning fossil fuels to obtain the necessary temperatures and pressure (up to 500 ° C and 200 pressure in the atmosphere), and release 450 megatone2 In the atmosphere every year (1.5 % of all Co2 Emissions7. Moreover, excess chemical fertilizers that flow into rivers, lakes and oceans cause algae flowers, which enhances nitrous oxide emissions, which is a greenhouse gas more powerful than any Colorado2 Or methane.
Many bacteria and Arkia can be used to produce nitrogen fertilizer with much lower greenhouse gas emissions than artificial fertilizers. This is because microbes repair nitrogen at room temperature and at sea pressure at the sea level using enzymes known as nitrogen that transforms nitrogen in the atmosphere (N.2) In Ammonia (nh3).
Many companies are now selling vital crops, which contain combinations that contain bacteria called Risobia or other microbes that can increase the availability of foodstuffs for plants (see “Towards the Biopathy” and go.nature.com/3fs2xqf). An increasing number of biomedic microbials also provides food producers as a way to control8.
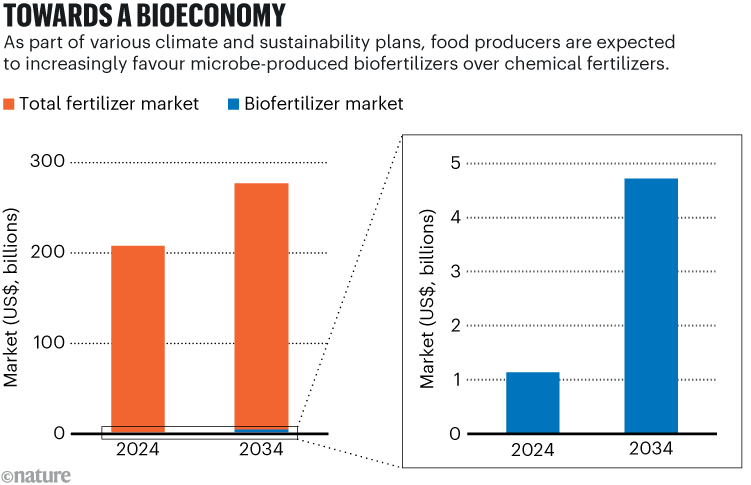
source: https://www.precedenceresearch.com/fertilizer- Market
Keep it safe
With more microbial solutions to the market-whether vital or naturally existing-is naturally biomusic considerations.
It has been shown that many solutions, such as the use of bacteria to deteriorate crude or plastic oil, are effective and safe in a laboratory environment9. However, the increase in its use of the levels needed to reduce global emissions or the loss of global biological diversity may lead to unexpected complications.
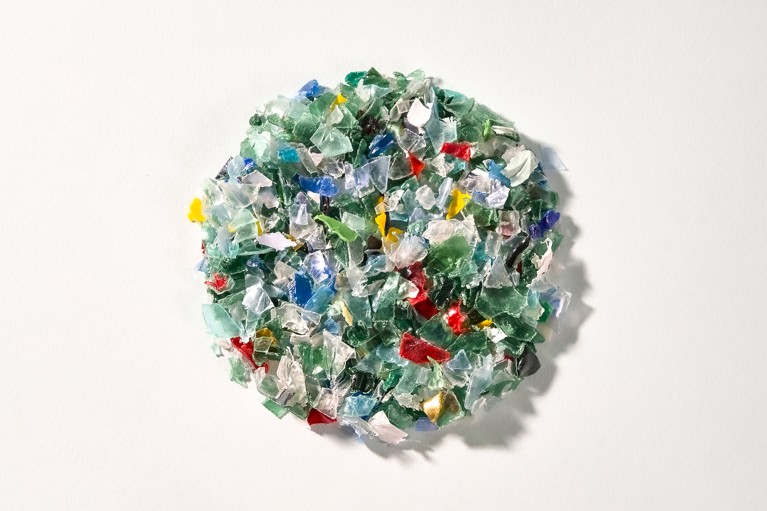

Bacteria are designed to break plastic waste.Credit: Carbios – Agencyskotchprod
Some guarantees are already developed – the design of bacteria that can continue in the ecosystem for only a short period or that can exist under specific environmental conditions only –4. In a similar way to give up clinical trials in biomedical research, laboratory experiments can follow tests contained in the external environment, which can then be followed by large -scale field tests. Researchers will also need to monitor systems over time, which may include environmental DNA sequence of wastewater and other methods used to monitor infectious infection.
Ultimately, effective publishing, containing and monitoring the vastly -based solutions to scientific societies, governments and companies will require the development of evidence -based policies, and to engage in clear and transparent communication about enormous opportunities and potential risks.
